Key Takeaways
• India’s Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 was approved in Parliament by April 2, 2025, replacing four older laws.
• The law creates a Bureau of Immigration, uses AI biometric systems, and mandates digital registration for foreigners over 180 days.
• Strict penalties apply for illegal entry, overstaying, forgery; new visa categories support business, startups, skilled workers, and digital nomads.
Summary and Effective Date
India’s Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 marks a major overhaul of the country’s immigration laws. The bill was introduced in the Lok Sabha on March 11, 2025, passed by the lower house on March 27, and approved by the Rajya Sabha on April 2, 2025. With parliamentary approval complete, the law is now in the final stages before full implementation, expected to begin in the coming months. This new framework replaces four older laws and introduces sweeping changes to how India 🇮🇳 manages the entry, stay, and exit of foreign nationals.
Background and Reasons for the Bill
The Indian government has described the Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 as a modernization effort, aiming to bring the country’s immigration system in line with global standards and economic ambitions. However, the timing and content of the bill also reflect rising concerns about “undesirable outsiders”—a term that has gained traction in political and media discussions.
Several factors led to the introduction of this bill:
- Security Concerns: Recent geopolitical tensions and incidents along India’s borders have heightened worries about national security. The government has linked illegal immigration to potential threats, especially from neighboring countries.
- Economic Goals: India seeks to attract global talent, investment, and innovation. The new law introduces visa categories designed to support business, startups, and skilled professionals.
- Administrative Modernization: The previous patchwork of laws was seen as outdated and difficult to enforce. The new bill aims to centralize and digitize immigration management.
- Political Climate: Nationalist sentiment has been on the rise, with calls for stricter border controls and a more assertive approach to immigration.
Affected Aspects of Law
The Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 consolidates and replaces four key pieces of legislation:
– The Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920
– The Registration of Foreigners Act, 1939
– The Foreigners Act, 1946
– The Immigration (Carriers’ Liability) Act, 2000
Key changes introduced by the bill include:
- Creation of New Authorities: The law establishes a Bureau of Immigration to oversee all immigration functions, and a National Immigration Authority (NIA) to manage policy and maintain a centralized digital database.
- Integrated Digital System: The Integrated Immigration Management System (IIMS) will use biometric identification and artificial intelligence to track and monitor foreign nationals.
- Stricter Entry Requirements: All foreigners must have valid passports and visas, and must enter and exit through designated immigration posts.
- Mandatory Digital Registration: Foreign nationals staying in India for more than 180 days must register digitally.
- Reporting Obligations: Hotels, universities, and hospitals must report the presence of foreign nationals to authorities.
- Specialized Visa Categories: New visa types are introduced to support business, startups, skilled workers, investors, transit travelers, and digital nomads.
- Harsher Penalties: The law imposes strict penalties for unauthorized entry, overstaying, and using forged documents. Transport carriers can also be penalized for failing to verify passenger documents.
Implications for Different Groups
The new law will have wide-ranging effects on various groups, both within India and abroad.
1. Undocumented Migrants and Refugees
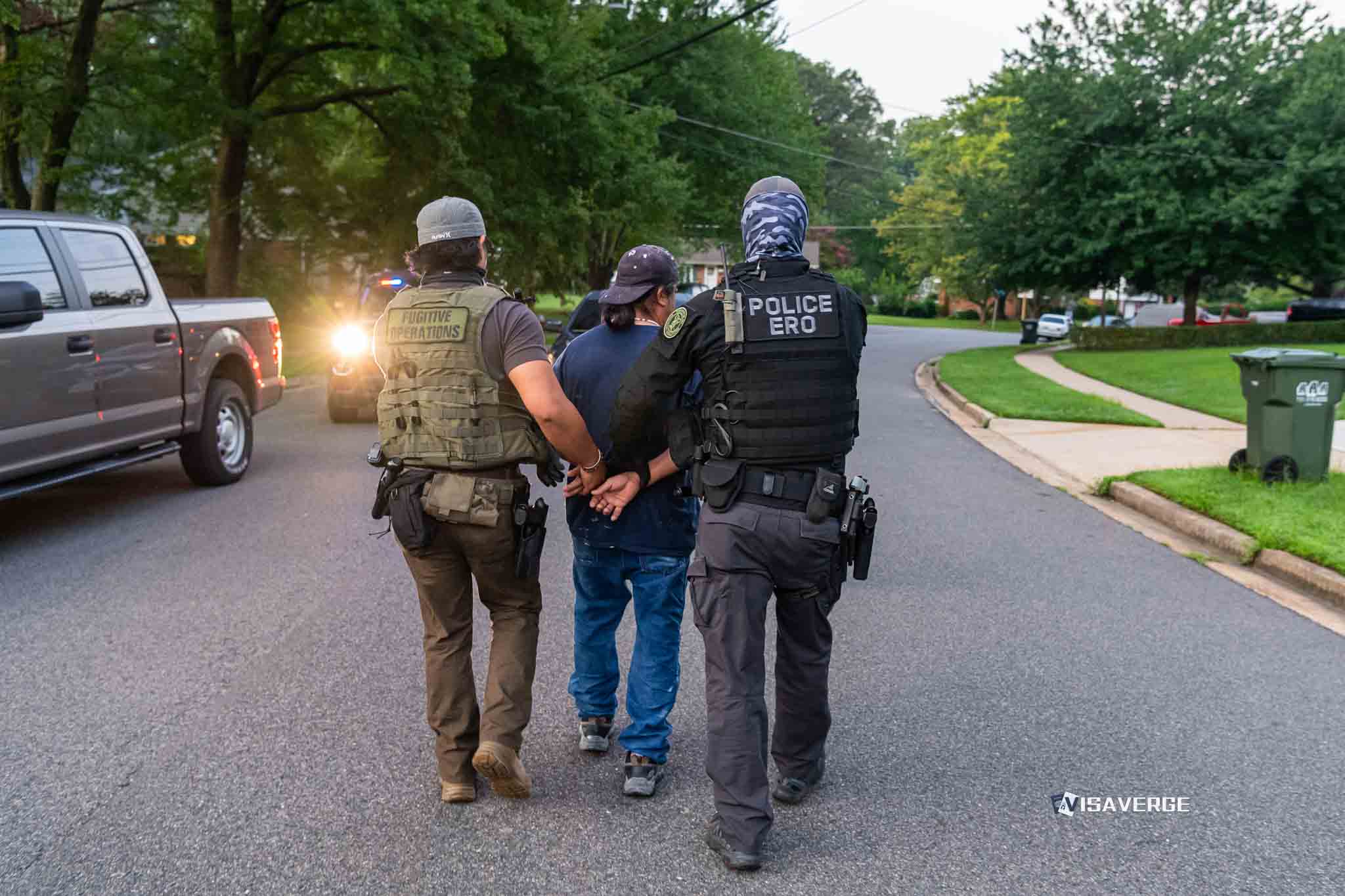
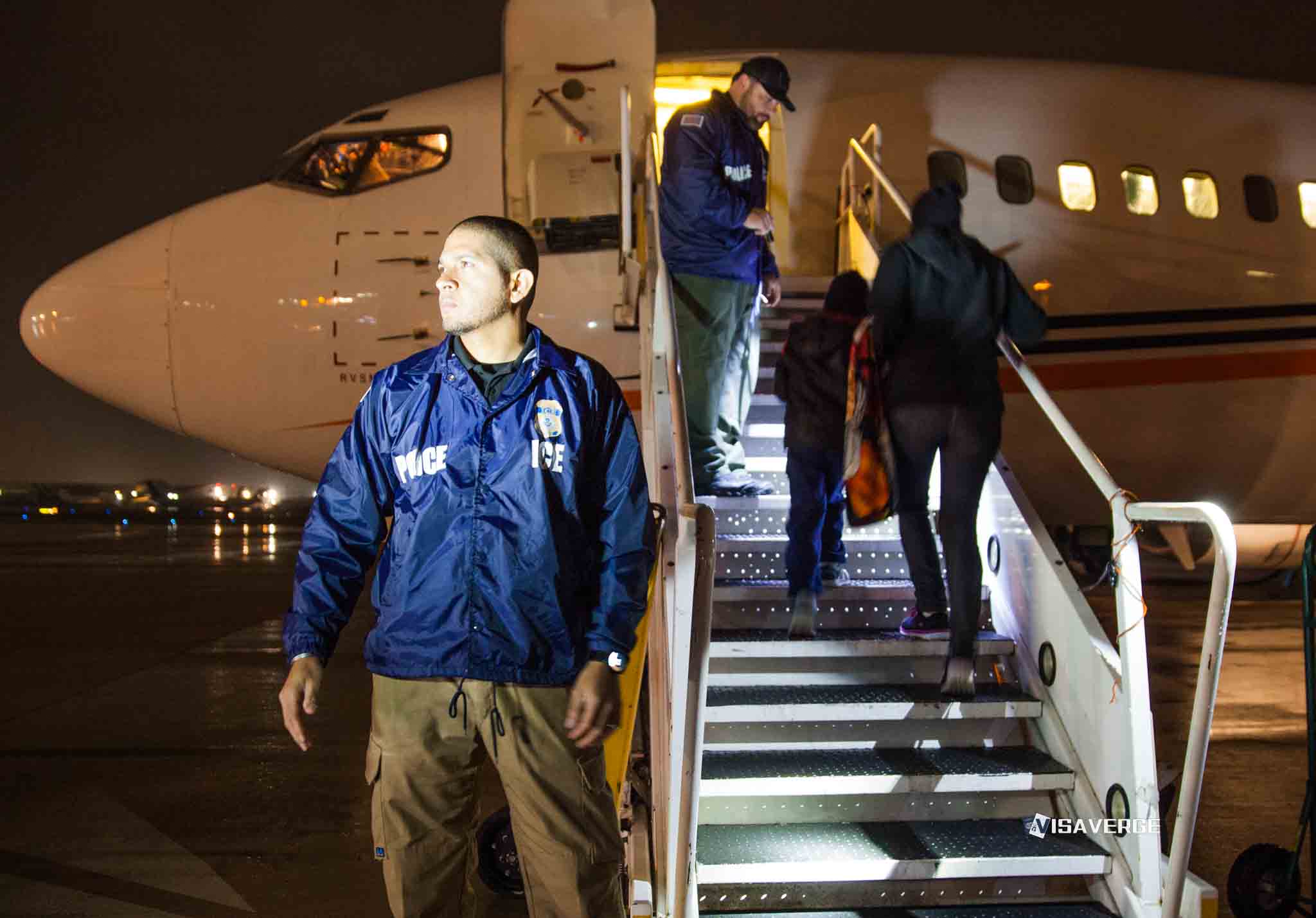
- Increased Enforcement: State governments have already begun rounding up undocumented individuals, particularly Bengali-speaking working-class people. The central government has launched a nationwide verification process, requiring completion within 30 days. Those found without proper documentation face deportation.
- Loss of Refugee Protections: The Supreme Court’s recent dismissal of the value of UNHCR refugee cards signals a shift away from recognizing international refugee protections. The government plans to end the policy of accepting UNHCR cards as valid identification, leaving many refugees—especially Rohingya—vulnerable to deportation.
- No Asylum Law: The bill does not introduce a comprehensive asylum or refugee protection framework, leaving stateless and persecuted groups without legal safeguards.
Example:
A Rohingya family living in Delhi with UNHCR cards may now face deportation, as these cards are no longer recognized. Without a national asylum law, they have no legal avenue to claim protection in India.
2. Foreign Workers, Students, and Business Travelers
- New Visa Options: The introduction of Business Visa Plus, Startup Visa, Skilled Talent Visa, Investor Visa, Transit Visa, and Digital Nomad Visa creates new pathways for those seeking to work, invest, or study in India.
- Digital Compliance: Foreign nationals must register digitally if staying over 180 days, and institutions hosting them must report their presence.
- Stricter Penalties: Overstaying or using forged documents can result in imprisonment and heavy fines.
Example:
A US-based entrepreneur seeking to launch a startup in Bengaluru can now apply for a Startup Visa, but must ensure all documentation is in order and comply with digital registration requirements.
3. Indian Businesses and Employers
- Compliance Burden: Companies must adapt internal systems to meet new digital reporting and verification standards. Failure to comply can result in penalties.
- Talent Mobility: The new visa categories may help companies attract foreign talent, but the stricter enforcement environment could deter some applicants.
Example:
A multinational IT firm in Hyderabad hiring foreign engineers must ensure all hires are registered in the new digital system and that their visas match the new categories.
4. Transport Carriers
- Liability for Passengers: Airlines and other carriers must verify that all passengers have valid travel documents. Failure to do so can result in fines or even seizure of vehicles.
Comparison with Previous Law
The Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 represents a sharp departure from the previous legal framework:
- Centralization: The new law centralizes authority under the Bureau of Immigration and NIA, replacing a fragmented system managed by multiple agencies.
- Digitalization: The IIMS introduces biometric and AI-based monitoring, whereas previous laws relied on manual processes.
- Expanded Penalties: Penalties for violations are much harsher, with longer prison terms and higher fines.
- Narrower Refugee Protections: The old system, while limited, allowed some flexibility for refugees with UNHCR cards. The new law removes this recognition, leaving refugees more exposed.
- New Visa Categories: The previous system had fewer, less specialized visa options. The new categories are designed to align with economic policy but may also increase scrutiny.
Implementation Timeline
- Immediate Steps: State governments have already begun enforcement actions, including verification drives and detentions.
- 30-Day Verification: The central government’s verification process for undocumented migrants is to be completed within 30 days of the law’s effective date.
- Digital Infrastructure Rollout: The IIMS and digital registration systems are expected to be operational within the next few months.
- Further Guidance: The National Immigration Authority will issue detailed rules and procedures as the law comes into force.
Critical Perspectives and Concerns
The Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 has sparked debate among legal experts, human rights advocates, and the international community.
Refugee and Human Rights Concerns
- No Asylum Law: India remains without a national asylum law, leaving refugees at risk of arbitrary detention and deportation.
- Targeting Vulnerable Groups: The law’s focus on “national security” and “undesirable outsiders” has led to profiling of certain ethnic and religious groups, especially Bengali-speaking Muslims and Rohingya.
- Alignment with Global Trends: The bill mirrors restrictive immigration policies seen in the United States 🇺🇸 under President Trump and in parts of Europe and Australia 🇦🇺, where AI-based tracking and stricter penalties are becoming common.
Political and Social Context
- Nationalist Rhetoric: Statements by officials, such as Home Minister Amit Shah’s assertion that India is not a “Dharamshala” (inn), reflect a hardening stance against outsiders.
- Operation Sindoor: Recent enforcement actions have coincided with military operations against Pakistan 🇵🇰, fueling perceptions that immigration policy is being used as a tool of national security.
Economic and Business Implications
Despite criticism, the government and business leaders argue that the new law will benefit India’s economy:
- Attracting Talent and Investment: Specialized visas are intended to bring in skilled workers, entrepreneurs, and investors.
- Boosting FDI and Innovation: By streamlining visa processes and introducing digital systems, the government hopes to make India more attractive to global business.
- Compliance Challenges: Companies must quickly adapt to new reporting and verification requirements.
Example:
A German investor interested in India’s renewable energy sector can now apply for an Investor Visa, but must navigate the new digital systems and stricter documentation checks.
Global Context and Comparisons
India’s new law fits into a broader global pattern:
- United States 🇺🇸: The bill’s strict penalties and focus on national security echo policies from the Trump administration, which emphasized border control and rapid deportation.
- Australia 🇦🇺: Like Australia’s recent tightening of student and work visa rules, India is increasing scrutiny of foreign nationals.
- Europe: The use of AI and biometric tracking aligns with trends in European countries seeking to monitor and control migration more closely.
Implementation Challenges and Next Steps
As the Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 moves toward full implementation, several issues remain:
- Legal Challenges: Human rights groups are likely to challenge aspects of the law, especially those affecting refugees and stateless persons.
- Clarification Needed: The government must provide clear guidance on registration protocols, enforcement procedures, and the operation of the new digital systems.
- Potential for Discrimination: There are concerns that the law could be used to target specific communities, leading to social tension and international criticism.
Practical Guidance for Stakeholders
- Foreign Nationals: Ensure all travel documents are valid and up-to-date. If staying in India for more than 180 days, complete digital registration as soon as the system is available.
- Refugees and Asylum Seekers: Be aware that UNHCR cards may no longer be recognized. Seek legal advice and monitor updates from refugee support organizations.
- Employers and Institutions: Review internal compliance systems and prepare for new reporting requirements. Stay informed about visa category changes and digital infrastructure rollouts.
- Transport Carriers: Implement strict document verification procedures for all passengers traveling to India.
Official Resources
For authoritative information and updates on the new law, visit the Bureau of Immigration, Government of India.
Conclusion
The Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 is a landmark piece of legislation that will reshape India’s approach to immigration for years to come. While the government touts its benefits for national security and economic growth, critics warn of the risks to vulnerable populations and the potential for abuse. As the law is implemented, all affected groups—immigrants, refugees, businesses, and institutions—must stay informed and prepared for significant changes. According to analysis by VisaVerge.com, the coming months will be crucial in determining how the new framework balances security, economic opportunity, and human rights in India’s evolving immigration landscape.
Learn Today
Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 → India’s new law replacing four older laws to modernize immigration management and enforcement.
Bureau of Immigration → A centralized authority established by the new law to oversee immigration processes in India.
Integrated Immigration Management System (IIMS) → A digital platform using biometrics and AI to track and manage foreign nationals.
UNHCR refugee cards → Identification documents issued by the UN Refugee Agency, losing official recognition under the new law.
Digital Nomad Visa → A new visa category for remote workers residing temporarily in India under the 2025 law.
This Article in a Nutshell
India’s 2025 Immigration Bill modernizes immigration laws with digital systems, stricter enforcement, and new visas. It aims to boost security and economic growth while sparking concern over refugee protections. Implementation begins soon, requiring compliance from migrants, businesses, and carriers. This law marks a pivotal shift in India’s immigration policy framework.
— By VisaVerge.com
Read more:
• NBAA celebrates House passage of budget bill for business aviation
• Air Europa sale stalls as Lufthansa Group rejects €1 billion valuation
• Trump’s Immigration Bill Slaps New Remittance Tax
• FAIR backs House Reconciliation Bill for record border security funding
• Reconciliation Bill Slams Immigrants With Tough New Limits








