The H-1B visa lottery system, designed to fairly allocate skilled-worker visas to deserving applicants, has become a rigged game that systematically disadvantages legitimate employers and workers while enriching a network of middlemen who exploit regulatory loopholes. Bloomberg’s investigation reveals that approximately one out of every six H-1B visas awarded in recent years were obtained through fraudulent gaming tactics, representing a $95 million annual theft from skilled workers and a fundamental corruption of America’s high-skilled immigration pipeline.
How the H-1B Lottery is Being Systematically Gamed
The Multiple Registration Fraud Scheme
The most prevalent form of H-1B gaming involves “multiple registration” – a practice where the same individual worker is entered into the lottery numerous times by different companies to artificially inflate their chances of selection. This scheme became rampant after USCIS introduced a streamlined registration process in 2020, reducing the entry fee to just $10 and eliminating the need to submit full documentation upfront.
The scale of this abuse is staggering. In one documented case, staffing firm operator Kandi Srinivasa Reddy used a dozen shell companies to enter the same applicants up to 15 times in a single lottery. His network of companies secured hundreds of H-1B visas while legitimate applicants who played by the rules were systematically excluded. By 2023, more than half of all lottery entries involved workers whose names had been submitted multiple times.
Outsourcing Firm Dominance of the System
Major outsourcing companies have transformed the H-1B program from its intended purpose of filling genuine skill shortages into a mechanism for labor arbitrage and job offshoring. These firms leverage their massive overseas workforces to flood the lottery with applications, crowding out smaller employers and legitimate direct hires.
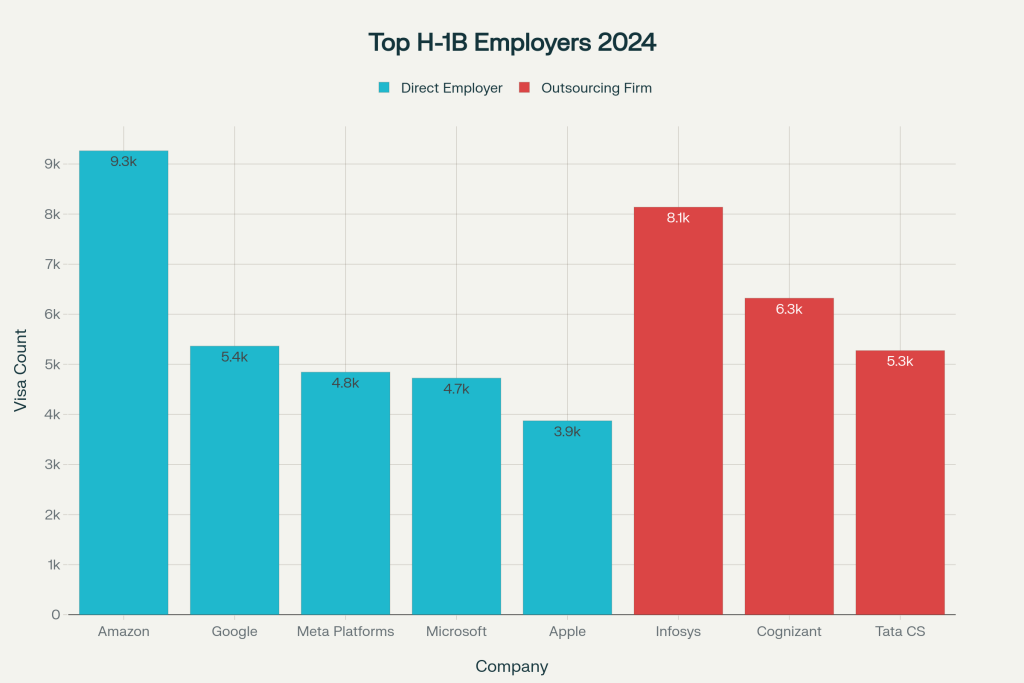
The data reveals how outsourcing firms have captured a disproportionate share of H-1B visas. In fiscal year 2023, 17 of the top 30 H-1B employers were outsourcing firms, receiving nearly 20,000 visas – almost one-quarter of the entire annual allocation of 85,000 visas. Companies like Cognizant Technology Solutions strategically over-apply, requesting nearly three times more visas than they actually need, knowing they can achieve close to 100% success rates while legitimate employers face rejection.
Wage Suppression Through Gaming
The gaming of the H-1B system has created a two-tiered wage structure that systematically underpays skilled workers. Research shows that 60% of all H-1B jobs are assigned wage levels well below the local median wage, with computer occupations paying 17% to 34% lower than local median salaries.
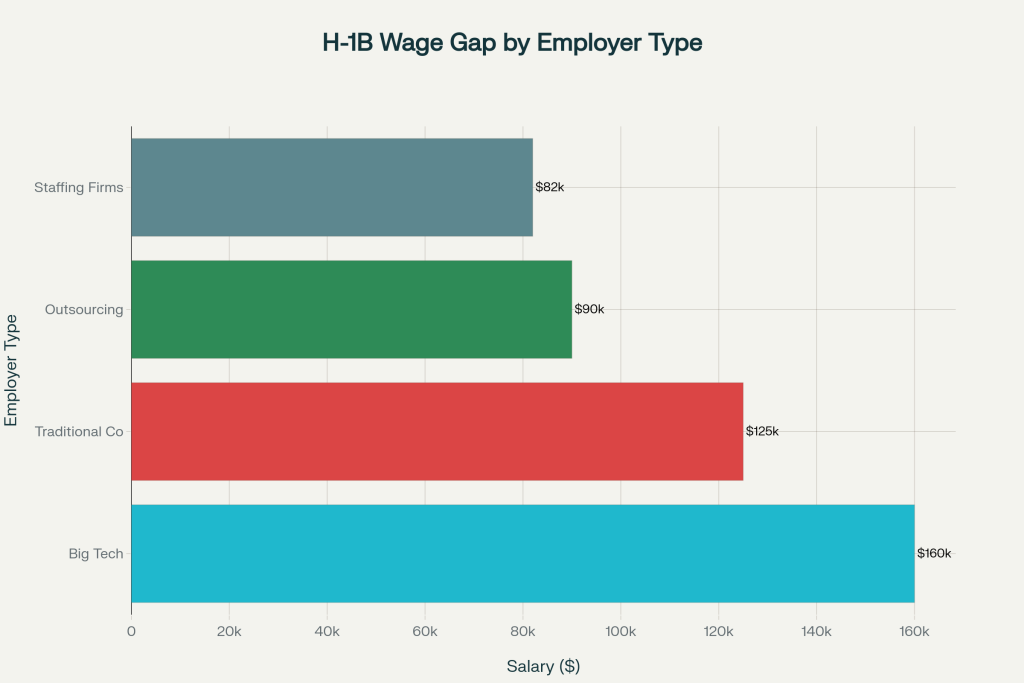
The wage disparity between direct hires and contracted workers is stark. While big tech companies pay their H-1B workers median salaries of $160,000, outsourcing firms pay only $90,000, and staffing firms pay as little as $82,000. This $95 million annual wage theft represents “white-collar wage theft on a grand scale”, enabled by regulatory loopholes that treat contractor hires differently from direct employees.
Current State of the H-1B System
Recent Regulatory Changes
USCIS implemented significant rule changes in 2024 to combat multiple registration fraud. The new system selects unique individuals rather than picking randomly among employer entries, eliminating the advantage of submitting multiple registrations for the same worker. This change resulted in a dramatic 38% drop in lottery applications for fiscal year 2025, with an 88% decline in duplicate entries.
However, these reforms only address one aspect of the gaming problem. Staffing firms continue to exploit the system by submitting speculative applications for workers without confirmed job placements. These companies complete full applications only about 50% of the time after lottery selection, compared to 90% for legitimate employers.
Political Volatility and Enforcement
The H-1B program has become a political football, with denial rates fluctuating dramatically based on administrative priorities. Under the Trump administration, denial rates skyrocketed from 6% in 2015 to 24% in 2018, while the Biden administration reduced rates to as low as 2% in 2022.
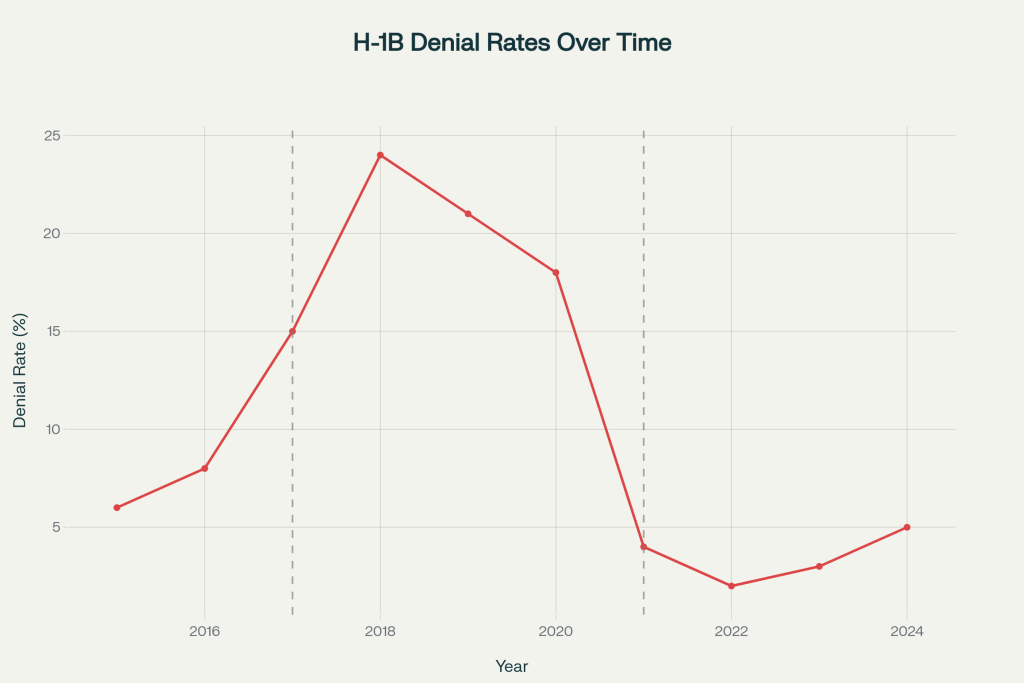
H-1B visa denial rates from 2015-2024, showing dramatic policy impacts under different administrations
This political volatility undermines program integrity and creates uncertainty for legitimate employers and workers. Despite documented fraud involving thousands of companies, USCIS lacks the authority to bar companies from future lottery participation, allowing repeat offenders to continue gaming the system with minimal consequences.
Why H-1B Reform Remains Politically Impossible
The Lobbying Industrial Complex
The H-1B program has spawned a massive lobbying apparatus that actively resists meaningful reform. Indian IT outsourcing companies have hired former Republican officials, including ex-governors and cabinet members, to influence U.S. policy. Research shows that firms’ immigration lobbying under the Trump administration reduced H-1B denial rates by 4.5 percentage points, demonstrating the direct impact of corporate influence on visa adjudication.
Major technology companies also lobby aggressively to maintain current rules that allow them to access lower-cost labor through outsourcing arrangements. Companies like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google routinely exceed prevailing wages for their direct hires while simultaneously using outsourcing firms that pay significantly less for similar work.
Competing Political Constituencies
Immigration reform faces a fundamental political paradox: the same policies that would fix H-1B gaming would also reduce overall visa availability, creating opposition from both pro-business and pro-immigration constituencies. Labor unions oppose expanding the program due to wage suppression concerns, while business groups resist restrictions that would limit their access to lower-cost workers.
The result is legislative paralysis. Despite bipartisan recognition that the system needs reform, Congress has not meaningfully updated H-1B rules since 2004. Proposed legislation like the H-1B and L-1 Visa Reform Act of 2023 remains stalled in committee, unable to overcome opposition from powerful lobbying interests.
Administrative and Enforcement Limitations
Federal agencies lack the tools and resources needed to effectively combat H-1B fraud. The Department of Labor has done “virtually nothing to ensure program integrity by enforcing wage rules”, while USCIS cannot bar companies from the lottery even after documenting fraud. This enforcement gap allows the outsourcing business model to flourish with minimal risk of serious consequences.
The complexity of modern corporate structures makes it easy for bad actors to create new shell companies and continue gaming the system even after being caught. Reddy’s network of firms, for example, received 15 new H-1B visas even after USCIS published a report documenting their scheme.
The Economic and Social Costs
Impact on American Workers
The gaming of the H-1B system has created a race to the bottom in skilled labor markets. When employers can access H-1B workers at below-market wages through outsourcing arrangements, it reduces incentives to train American workers or offer competitive compensation. Research suggests that for every 10 H-1B visas that legitimate employers lose to gaming, 9 jobs are moved offshore.
Harm to Legitimate H-1B Workers
The current system also exploits the very workers it claims to help. Staffing firms routinely charge workers for visa fees, withhold pay, and force workers to sign contracts preventing them from changing employers. Workers are afraid to report violations because complaints could jeopardize their visa status, creating conditions ripe for abuse.
Broader Economic Consequences
The Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond estimates that reducing high-skilled immigration by 10% would shrink the U.S. economy by $86 billion. By allowing gaming to corrupt the H-1B system, the United States loses access to genuinely skilled workers who could drive innovation and economic growth, while simultaneously enabling a form of labor trafficking that undermines wage standards for all workers.
A System in Crisis
The H-1B lottery has evolved from a tool for accessing global talent into a sophisticated mechanism for labor arbitrage that serves neither American workers nor legitimate immigrants. The gaming tactics documented by Bloomberg and other investigations represent a fundamental corruption of the system’s core purpose, enabled by regulatory gaps and sustained by powerful lobbying interests.
While recent USCIS rule changes have eliminated some forms of fraud, they represent only incremental progress on a problem that requires comprehensive reform. True reform would require Congress to act decisively against entrenched interests, close the outsourcing loopholes that enable wage suppression, and restructure the program to prioritize genuine skill shortages over corporate cost-cutting.
Without such action, the H-1B program will continue to serve as what critics aptly call “the outsourcing visa” – a system that enriches middlemen, exploits workers, and undermines America’s competitive position in the global economy. The question is not whether reform is needed, but whether the political system has the will to overcome the powerful interests that profit from the status quo.








